

The first stop on our battery-life betterment tour is the Windows battery performance slider, a recent addition to Windows 10. It aims to group all of the settings that affect battery life into a few easy-to-understand categories. The company that made your PC determines exactly which settings the battery slider controls. But in general, keep these guidelines in mind:
The Best Performance mode is for people willing to trade off battery runtime to gain performance and responsiveness. In this mode, Windows won’t stop apps running in the background from consuming a lot of power.
The Better Performance setting limits resources for background apps, but it otherwise prioritizes power over efficiency.
Better Battery mode delivers longer battery life than the default settings on previous versions of Windows. (It’s actually labeled “Recommended” on many PCs.)
Battery Saver mode, a slider choice that will appear only when your PC is unplugged, reduces the display brightness by 30 percent, prevents Windows update downloads, stops the Mail app from syncing, and suspends most background apps.

On the other hand, if you’re writing a novel or playing a local video file and don’t need to be distracted by notifications, it’s fine to enable Battery Saver. It’s a good habit to adjust your laptop use in more battery-conserving ways, such as by sticking to one app at a time and closing everything else when you’re not using it. It’s a bit like turning off the lights when a room is vacant. If you’re going back and forth between the kitchen and the pantry all the time, or between Firefox and Word, by all means keep both sets of lights and apps on and open. But if you’re just cooking or watching a YouTube video, you’ll be best served by turning off and closing everything else.
In addition to aiming to single-task, consider enabling Airplane mode in Windows, or turning off Wi-Fi and Bluetooth in macOS if you know you’ll be editing a document with no need for web access. In addition to eliminating distractions, Airplane mode eliminates a significant source of battery drain: not only the wireless radios themselves, but also the background apps and processes that constantly use them, such as updaters and push notifications.
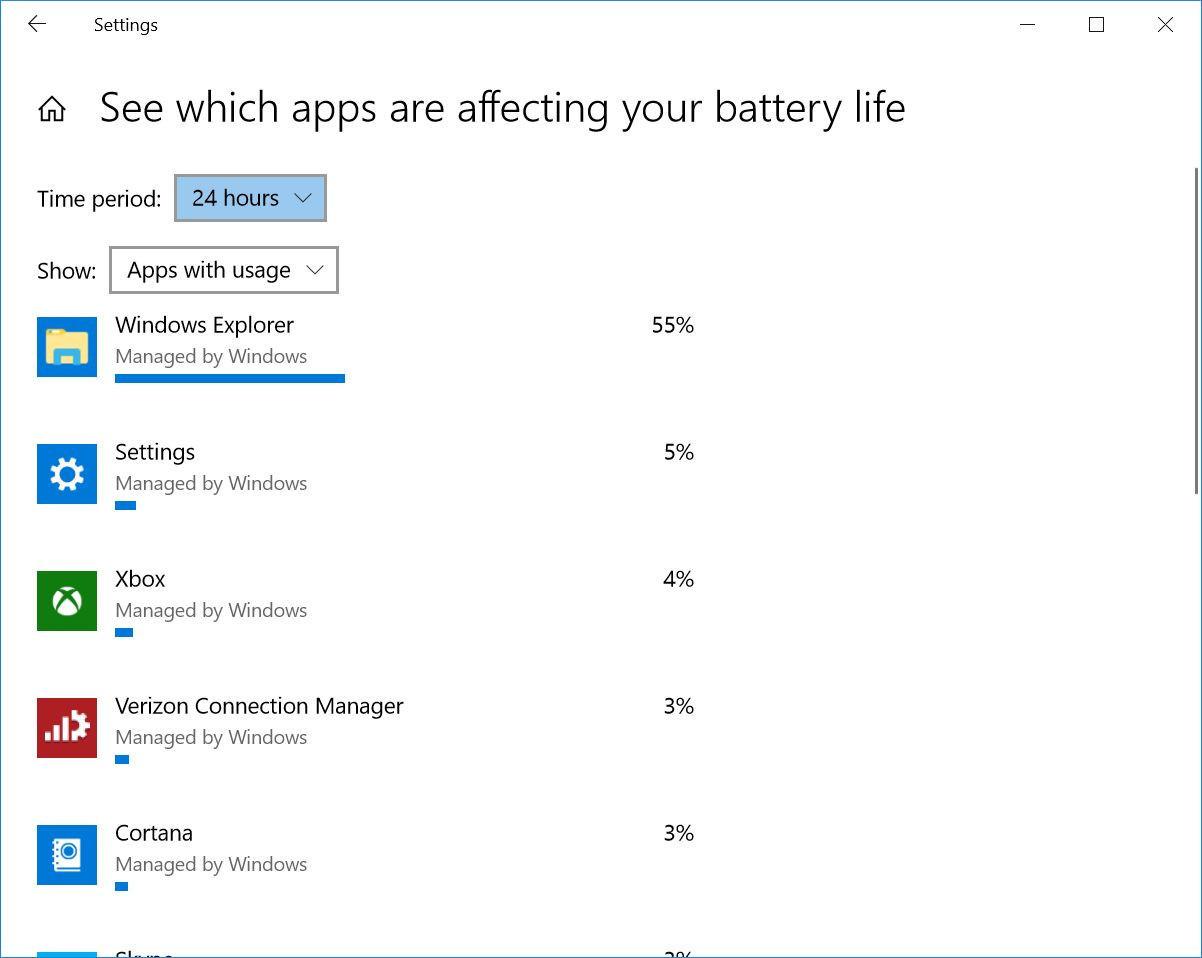
Type “see which apps are affecting your battery life” into the Windows search bar for a list of apps that are consuming the most power. If you see an app that you rarely use hogging a lot of power, make sure you close it. Often, these are apps you’ve opened in the background and forgot about, such as Spotify or Adobe Reader.
Next, type “See which processes start up automatically when you start Windows” into the search bar. This will open the Task Manager’s Startup tab, which lists every utility that runs as soon as you start your PC. Anything with a name like “Download Assistant” or “Helper” is usually safe to disable. For example, unless you frequently open Spotify playlists, tracks, or albums from links in a web browser, you can disable the Spotify Web Helper.

You do have to be careful about heat, however, which will hasten a battery’s demise. The biggest problems come from physical obstruction of the ventilation ports. Dust buildup is one problem, which you can take care of by cleaning the laptop’s vents and fan. (Periodically, use a can of compressed air to blow out some of the dust.) A more frequent issue that crops up, though, is using the laptop on a pillow or blanket, which can both obstruct the ventilation fan and retain the heat coming off of the system. Avoid this by using your laptop only on firm surfaces such as a table or a desk, which won’t flex and block airflow or cooling.


These external power sources plug in to your laptop the same way your charger does. They generally cost between $100 and $200, but come with adapters for use with many different laptop models. They can be used on more than one system, and even for other devices, such as your phone or tablet.